DeFi, a blockchain-based financial system, revolutionizes traditional banking by providing transparent, trustless services. However, its increased adoption necessitates robust security measures to protect transactions and smart contracts. 1. Immutability and Tamper Resistance One of the defining security features of blockchain technology is immutability—once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This feature ensures that transaction histories remain transparent and tamper-proof, preventing fraudulent behavior. In DeFi, immutability gives users confidence that malicious actors cannot manipulate their funds and transactions. This is particularly beneficial for auditing purposes, as every transaction is permanently stored and can be verified on the blockchain, enhancing trust and accountability. 2. Decentralization: Eliminating Single Points of Failure Traditional financial systems rely on centralized servers, making them vulnerable to attacks or system failures. In contrast, blockchain technology operates on a decentralized network of nodes that validate and maintain the ledger. This decentralized structure ensures that no single entity can control or compromise the system. In DeFi, decentralization also means that smart contracts execute transactions without intermediaries. Removing intermediaries reduces the risk of data breaches, fraudulent activities, and the possibility of service disruptions caused by centralized failures. 3. Smart Contracts for Automated Security Smart contracts are the backbone of DeFi platforms, enabling automated and trustless transactions. These self-executing contracts contain predefined rules and conditions that must be met for a transaction to occur. Smart contracts..
Read MoreThis blog discusses the role of blockchain architects in the rapidly growing DeFi ecosystem, highlighting their crucial role in ensuring the success and security of decentralized platforms and their responsibilities in DeFi projects. 1. What is a Blockchain Architect? A blockchain architect is a highly skilled professional responsible for designing, developing, and implementing blockchain solutions. They ensure blockchain technology integrates seamlessly with a company's business operations or a project’s decentralized objectives. In the DeFi space, blockchain architects focus on building and maintaining decentralized platforms that provide financial services without intermediaries, such as lending, borrowing, trading, or earning interest through cryptocurrency. While blockchain developers write and test code, blockchain architects take a higher-level view of the project. They plan the overall architecture and ensure that the blockchain infrastructure is scalable, secure, and effective in achieving its goals. 2. Core Responsibilities of a Blockchain Architect in DeFi Blockchain architects play a critical role in DeFi by providing the technical framework for decentralized platforms. Their key responsibilities include: Designing the Blockchain Framework: Blockchain architects create the foundation for a decentralized platform by developing the underlying blockchain structure. This includes choosing the consensus mechanism (e.g., Proof of Stake or Proof of Work), selecting appropriate cryptographic algorithms, and ensuring the platform can scale efficiently as the user base grows. Intelligent Contract Design: Since DeFi platforms rely heavily on smart contracts to automate transactions and processes,..
Read MoreInteroperability in blockchain refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate, share data, and transfer assets seamlessly. Traditionally, most blockchains functioned in isolation, limiting interaction between networks. This lack of connectivity has posed challenges for the Decentralized Finance (DeFi) ecosystem, where cross-chain transactions and interoperability are critical for growth and scalability. However, with advances in blockchain interoperability, DeFi platforms are evolving, offering users greater flexibility, efficiency, and innovation. Here’s how blockchain interoperability transforms DeFi and opens new opportunities for decentralized finance. 1. What Is Blockchain Interoperability? Blockchain interoperability refers to the ability of multiple blockchain networks to interact with one another, allowing assets, data, and smart contracts to flow across chains without restrictions. This connectivity eliminates relying on single-chain ecosystems, making DeFi platforms more robust and accessible. Interoperability tools such as cross-chain bridges, oracles, and Layer 2 solutions facilitate asset transfers and data exchange between different networks, such as Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Polkadot. 2. Unlocking Cross-Chain Transactions in DeFi One of the most significant benefits of interoperability is cross-chain transactions, where users can transfer tokens or assets from one blockchain to another without intermediaries. For example, with cross-chain bridges, users can transfer Bitcoin (BTC) to Ethereum and participate in Ethereum-based DeFi protocols using wrapped BTC (WBTC). This flexibility allows users to access DeFi services like lending, staking, and liquidity pools across multiple blockchains, expanding their earning..
Read MoreThe need for resilient blockchain networks grows as digital assets like cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and tokenized securities become increasingly popular. Blockchain resilience ensures these networks remain secure, decentralized, and operational even under stress from cyberattacks, network failures, or high transactional loads. In this blog, we explore the key strategies and technologies blockchain architects use to build robust networks capable of supporting the growing demands of digital assets. 1. Decentralization for Fault Tolerance A core principle of blockchain resilience is decentralization. In a decentralized network, multiple nodes process and validate transactions, ensuring the system does not rely on a single point of failure. If some nodes go offline or are compromised, the network can still function through other operational nodes. Example: Networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum use thousands of nodes, ensuring that the blockchain remains secure and operational even if some nodes fail. Impact: Decentralization strengthens fault tolerance, enabling the blockchain to remain operational despite disruptions or attacks. 2. Consensus Mechanisms to Ensure Network Integrity Blockchain resilience relies on effective consensus mechanisms that maintain the accuracy and integrity of transactions. Popular consensus algorithms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). These mechanisms make it difficult for malicious actors to manipulate the network, ensuring its resilience. Example: Ethereum’s shift from PoW to PoS reduced energy consumption and improved security, increasing the network’s ability to handle large-scale adoption. Impact: Reliable consensus..
Read MoreAs Decentralized Finance (DeFi) grows, scalable solutions become essential. Blockchain architects are critical in designing and implementing systems that handle increasing demand without compromising performance, security, or decentralization. In this blog, we explore how blockchain architects build scalable DeFi platforms, their challenges, and their strategies to achieve seamless scalability. 1. The Role of Blockchain Architects in DeFi Solutions Blockchain architects are responsible for designing the infrastructure and framework for DeFi platforms. Their work involves selecting the appropriate blockchain protocols, optimizing intelligent contract functionality, and ensuring system interoperability. Their designs must support high transaction volumes, prevent bottlenecks, and align with decentralization principles. 2. Key Challenges in Scaling DeFi Platforms Scalability is a pressing concern in DeFi because public blockchains, like Ethereum, can become congested during peak activity. Issues such as high gas fees, transaction delays, and network bottlenecks must be addressed for DeFi applications to perform efficiently. Example: During a surge in DeFi activity, Ethereum gas fees spiked, making transactions expensive and deterring users from interacting with DeFi apps. Blockchain architects aim to design systems that can scale seamlessly, even during periods of high demand, without compromising speed or affordability. 3. Strategies for Building Scalable DeFi Solutions a. Layer-2 Scaling Solutions Layer-2 technologies, such as Rollups and State Channels, help DeFi platforms handle higher volumes by processing off-chain transactions and settling them on the main blockchain in batches. This reduces the..
Read MoreAs blockchain adoption grows, so does the need for faster, more efficient transaction processing. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platforms, in particular, require scalability to handle increasing user demand without compromising on decentralization or security. Enter Layer 2 solutions are designed to enhance blockchain scalability and efficiency by processing transactions off the main chain while maintaining the security of Layer 1. What Are Layer 2 Solutions? Layer 2 refers to secondary frameworks or protocols built on top of a blockchain’s base layer (Layer 1) to improve transaction throughput and reduce costs. While Layer 1 chains like Ethereum ensure decentralization and security, their limited scalability often results in network congestion and high fees. Layer 2 solutions alleviate these issues by processing most transactions off-chain while periodically settling them on Layer 1 for finality and security. Benefits of Layer 2 for DeFi Improved Scalability: Layer 2 reduces the load on the main blockchain, allowing DeFi platforms to handle more transactions per second (TPS). Lower Costs: By offloading transactions to Layer 2, users experience significantly reduced gas fees, making DeFi more accessible. Faster Transactions: Transactions on Layer 2 are processed in near real-time, enhancing the user experience for trading, lending, and other DeFi activities. Types of Layer 2 Solutions State Channels: State channels allow two parties to conduct multiple off-chain transactions, recording only the final state on the main chain. Use Case: Microtransactions or recurring..
Read MoreIn the digital age, how we create, buy, and sell art, music, and other creative works is revolutionizing. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) are at the forefront of this transformation, leveraging blockchain technology to provide artists, musicians, and creators with new opportunities to monetize their work and connect with audiences. By ensuring transparency, authenticity, and ownership, NFTs redefine how digital assets are valued and exchanged. 1. What Are NFTs? NFTs are unique digital assets stored on a blockchain. They typically represent ownership of art, music, videos, or other creative works. Unlike cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, which are interchangeable (fungible), NFTs are one of a kind, giving them intrinsic value. 2. NFTs in the Art World The art industry has quickly embraced NFTs, with digital artworks selling for millions of dollars. Blockchain technology ensures that artists can: Prove Authenticity: Each NFT contains metadata that verifies the creator and ownership history, reducing the risk of forgery. Earn Royalties: Smart contracts enable artists to earn a percentage of future sales, creating a sustainable revenue stream. Reach Global Audiences: Artists can showcase and sell their work on NFT marketplaces without needing traditional galleries. Example: Beeple’s digital artwork “Everyday: The First 5000 Days” sold for $69 million, highlighting the potential of NFTs in digital art. 3. Music and NFTs The music industry is transformed as NFTs empower artists to connect directly with their fans. Musicians can:..
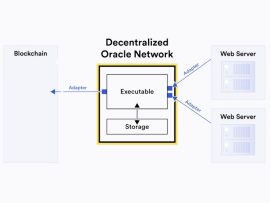
Read MoreDeFi revolutionizes financial systems by providing trustless, transparent alternatives. Oracle networks bridge on-chain and off-chain data gaps, enabling DeFi applications to operate effectively. 1. What Are Oracle Networks? Oracle networks are decentralized systems that fetch, verify, and deliver real-world data to blockchain-based smart contracts. Unlike traditional APIs, which operate within centralized frameworks, Oracle networks ensure the reliability and integrity of the data through decentralization and cryptographic proofs. 2. The Role of Oracles in DeFi DeFi applications rely on accurate and real-time data to execute smart contracts. oracle networks enable these applications to: Access Price Feeds: Lending platforms and decentralized exchanges (DEXs) depend on price feeds for cryptocurrencies, fiat currencies, and commodities. Oracles provide this data to ensure fair trading, accurate liquidation events, and proper collateralization. Example: Platforms like Aave and Uniswap use Oracle-provided price feeds for asset valuation. Enable Complex Financial Instruments: Products like derivatives, options, and insurance require dynamic inputs like weather data, interest rates, and stock prices. Oracles makes these advanced instruments possible by delivering off-chain data to the blockchain. Mitigate Risk: Oracles enhance security by delivering verified and tamper-proof data. For example, they prevent price manipulation attacks by aggregating data from multiple trusted sources. 3. Key Features of Oracle Networks in DeFi Decentralization: By decentralizing data sources and validators, oracle networks eliminate single points of failure, ensuring reliability and reducing the risk of malicious tampering. Data Integrity:..
Read MoreThe rise of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has opened up new possibilities in the financial sector, challenging traditional centralized systems. At the heart of DeFi lies blockchain technology, which allows users to interact, transact, and govern platforms without intermediaries like banks or financial institutions. However, blockchain projects differ in how they manage decision-making processes, with two main governance models: centralized and decentralized control. Understanding these models is crucial for anyone interested in the evolution of DeFi and its potential to reshape financial services. 1. Centralized Governance in DeFi In a centralized governance model, decision-making is controlled by a central authority or a small group of stakeholders. This centralized control is often seen in early-stage DeFi projects or protocols that require clear leadership and direction. Usually comprising founders or key stakeholders, the core development team decides upgrades, changes, and protocol rules. While centralized governance provides quick decision-making and more streamlined processes, it goes against the fundamental principles of decentralization that many DeFi projects aim to achieve. Pros of Centralized Governance: Faster decision-making process, with fewer participants involved in the decision. Clear leadership and accountability can be crucial in the early stages of development. Cons: Centralized control can lead to the centralization of power, potentially undermining the principles of decentralization. Risk of poor decision-making if the central authority is not aligned with the community’s best interests. 2. Decentralized Governance in DeFi On the..
Read MoreReal estate is one of the most lucrative and stable investment sectors. Still, it has traditionally been difficult for many investors to access, given high capital requirements and the complexities of property ownership. Blockchain technology, however, is changing the game by enabling real estate tokenization, a process that breaks down physical properties into digital assets or tokens. This innovation allows for fractional ownership, making investing in real estate with smaller amounts of capital easier for individuals. In this blog, we’ll explore the role of blockchain in real estate tokenization and how it is transforming the industry. 1. What is Real Estate Tokenization? Real estate tokenization refers to creating digital tokens on a blockchain representing ownership shares in a real estate asset. Each token represents a fraction of the property's total value, allowing investors to own a portion without purchasing the entire asset. These tokens are stored on a decentralized blockchain, ensuring transparency, security, and transaction efficiency. Example: Suppose a commercial building is valued at $10 million. Instead of a single investor purchasing the property, it can be tokenized into 1 million tokens, each worth $10. Investors can buy as many tokens as they like, thus owning a fractional share of the property. 2. Benefits of Tokenization in Real Estate a. Increased Liquidity One of the most significant advantages of tokenization is that it makes real estate more liquid. In traditional..
Read More